Encapsulation and Potting Resins: Frequently Asked Questions
Encapsulation and potting resins are materials used to cover electronic components for protection. In this article, we will address the most frequently asked questions about encapsulation and potting resins.
The global market for encapsulation and potting resins is estimated to reach a value of $3.6 billion by 2028, with a growth rate of 4.1% compared to 2021. The increasing adoption of consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and the electrification of modern cities is a major driver of market growth. This has led electronics manufacturers to invest in more efficient and innovative encapsulation and potting solutions to stand out in this rapidly expanding market.

Here are the most frequently asked questions about encapsulation and potting resins
What are the advantages of using encapsulation and potting resins?
Encapsulation resins offer crucial advantages to electronic systems, including:
- Temperature damage prevention: By dissipating heat generated within electronic assemblies, components are protected against overheating. Additionally, potential damage caused by cold-induced contraction is also avoided.
- Protection against moisture, chemicals, and environmental hazards: Encapsulation and potting resins seal electronic components, protecting them from exposure to moisture, humidity, water, dust, chemicals, pressure variations, and even physical handling.
- Protection against vibrations, shocks, or abrasion: This increases equipment lifespan and durability by reducing component damage, thus minimizing the need for maintenance and repairs.
- Electrical insulation: This occurs when resins replace air around the components, eliminating the risk of electrical fires.
How do encapsulation (potting) resins protect electronic components?
Encapsulation resins protect electronic components by covering them. Components are securely held within a resin mold, allowing them to function as intended without direct exposure to external hazards, forces, or contaminants. Additionally, the resin replaces the air around the electronic components, ensuring thermal management and eliminating the risk of sparks and combustion. Due to these factors, along with the mentioned advantages, electronic components are protected to a significant extent and can operate much more reliably.
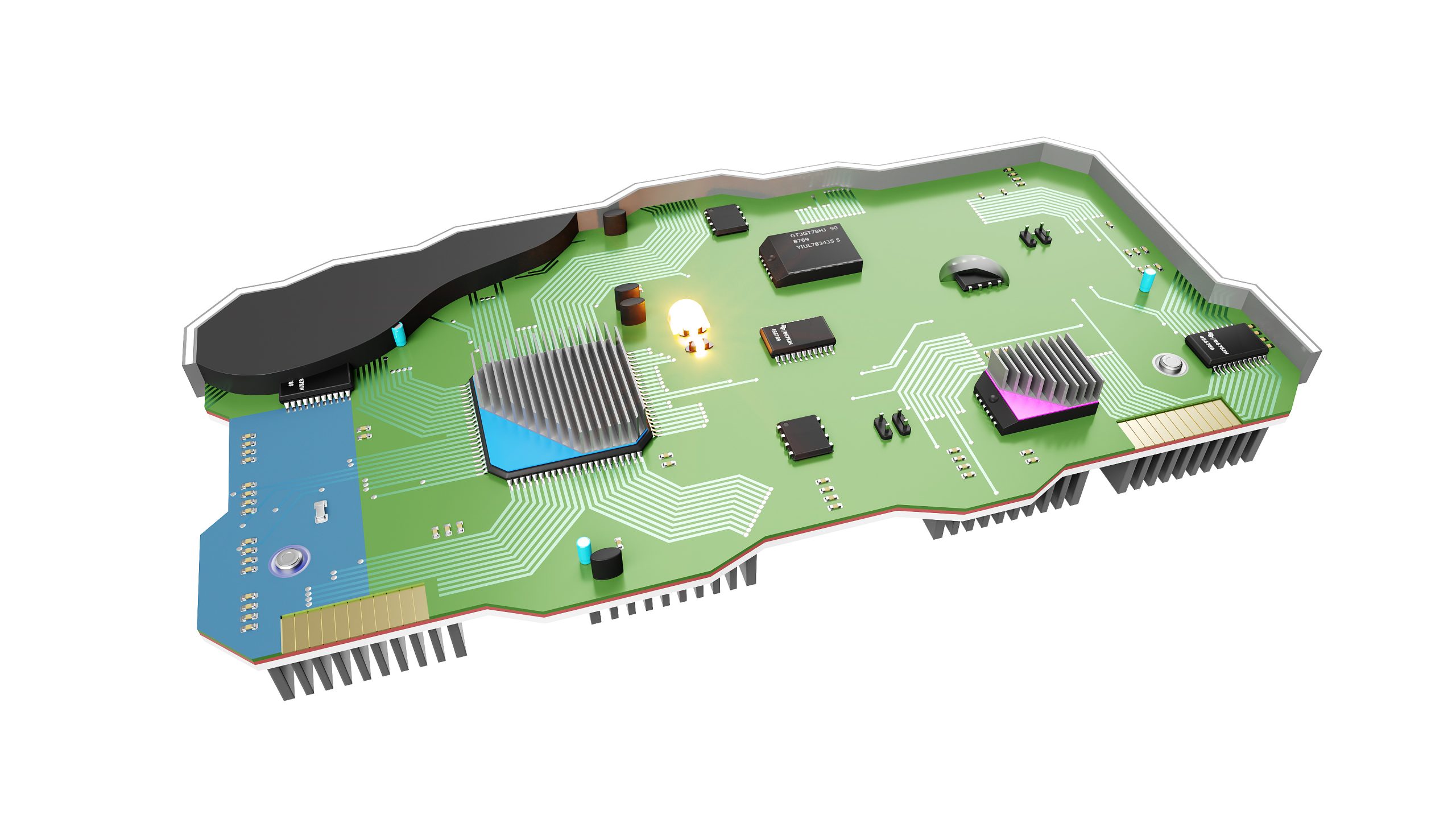
What are common causes of failure in encapsulation and potting resins?
Common causes of failure in encapsulation and potting resins include:
- Improper resin and hardener mixing.
- Incorrect resin deposition.
- Lack of surface preparation on substrates.
- Incorrect resin storage, such as in non-airtight containers.
- Improper degassing of resins.
- Incorrect resin curing.
How do encapsulation (potting) resins differ from conformal coatings?
Encapsulation and potting resins, as well as conformal coatings, can be used to protect electronic components. However, they have some differences, including:
- Encapsulation resins offer the most comprehensive protection for electronic components, making them ideal for applications requiring high mechanical stresses, exposure to chemical or environmental factors, as well as high thermal or electrical insulation.
- Encapsulation resins are waterproof, while only certain conformal coatings provide this feature.
- Conformal coatings provide a very thin and lightweight protective layer on components, whereas encapsulation resins are thicker and heavier resin layers.
- Conformal coatings can be processed and applied more easily, providing manufacturers with greater flexibility.
How do I choose an encapsulation resin for my application?
Important factors to consider when choosing an encapsulation resin for your application include:
- Specifications of the electronic component to be protected.
- Hazards the components need protection from (e.g., water, temperature, chemicals, etc.).
- Production and curing times.
- Fire resistance requirements (e.g., UL 94).
- Required stress tolerance.
- Thermal cycling within the components.
- Operating temperatures of the application.
- Component lifespan.
- Required flexibility in the application.
- Presence of physical impacts, shocks, and handling.
It is essential for manufacturers to choose an encapsulation resin that best matches these specifications in order to achieve comprehensive electronic protection.
What encapsulation and potting resins does Samaro offer?
At Samaro, we offer a wide range of encapsulation and potting resins for electronic protection applications.
Different types of encapsulation and potting resins are used depending on the desired electronic protection. Generally, there are three main types of encapsulants:
Silicones
Dow’s Dowsil™ and Sylgard™ brands offer moisture-resistant hydrophobic encapsulants with lower hardness than other chemistries to prevent stress relief. These silicone resins are used in challenging environments such as vibrations and thermal shocks. There are different types of silicone resins available, including:
- Room Temperature Vulcanization (RTV) and High Temperature Vulcanization (HTV) elastomeric silicone encapsulation resins.
- RTV and HTV silicone gel encapsulation resins.
- UV-curable silicone gel encapsulation resins.
These resins are characterized by high dielectric rigidity and a wide operating temperature range. Additionally, they are easy to work with as they are available in 1:1 or 10:1 mixing ratios.
Epoxy
Huntsman, through its Araldite® and Aradur® brands, has been offering widely used epoxy resins for many years. These resins are known for their hardness, strength, and low shrinkage during polymerization. They exhibit excellent mechanical performance, resistance to high temperatures, good adhesion to a wide range of substrates, and chemical resistance.
Different types of epoxy resins are available, including:
- Two-component hot-curing epoxy resins.
- Two-component semi-rigid room temperature-curing epoxy resins (Shore A70 to Shore D75).
- Two-component rigid room temperature-curing epoxy resins (Shore D80 to Shore D90).
These resins are available in bulk or kits. The kits include pre-measured containers of resin and hardener, ensuring the correct mixing ratio and eliminating the need for weighing components by the user.
Resin packs are also offered, which come in a plastic sachet divided into two compartments by a removable bar. The resin and hardener are pre-dosed at the correct ratio, allowing precise mixing of the two parts once the bar is removed, without introducing air. Additionally, the sachet can be used as a dispensing tool to accurately fill the targeted enclosure.
Polyurethane
Electrolube offers a wide selection of polyurethane encapsulants. These resins are particularly recommended in situations where the printed circuit board incorporates fragile components. Compared to epoxy resins, polyurethane resins generate less heat during curing.
Polyurethane encapsulants have an intermediate hardness, falling between silicone and epoxy resins, providing them with a certain degree of flexibility.
Moreover, these encapsulants are suitable for low-temperature applications and comply with UL standards.